The function of the cage is to separate the rolling elements and keep them equally spaced to minimize friction and heating. It also fulfils important complementary functions: • keep the rolling elements assembled with one ring in detachable component bearings such as tapered and cylindrical roller bearings, self-aligning ball bearings, spherical roller bearings, • help guide the rolling elements.
-Materials
The cages are produced from several materials using various manufacturing processes. For each bearing there is a standard type of cage, which has always proved satisfactory in service, and is considered to be the best design for the majority of applications. The standard cage used for large bearings may differ from that for small bearings within the same series because of the different applications, manufacturing processes and costs. When a cage type becomes a standard cage, it is no longer identified by a specific suffix in the SNR bearing designation
1).Molded synthetic material cages
The most commonly used material at present is polyamide 6.6 fiber glass reinforced. These cages display interesting mechanical characteristics: low friction coefficient, elasticity, good impact and vibration resistance. Furthermore, the molding process allows precise shapes that improve the guiding of the rolling elements. Due to the speed of changes in the world of synthetic materials, consult SNR for detailed information on the conditions of use of these cages. The SNR standard sealed or shielded bearings can be equipped with this type of cage and compatible grease.
2).Cages made of stamped mild steel or brass sheets
In one or two pieces, riveted, fold clamped or welded together. These cages can be given a surface treatment to improve the friction coefficient.
3).Machined cages: phenolic resin, copper base alloys, aluminium alloys
For large-sized cages produced in small quantities, the machined brass cage is often standard, and in this case the bearing reference is always followed by the cage suffix (M, MA, or MB).
-Cage centering
The cages can be centered:
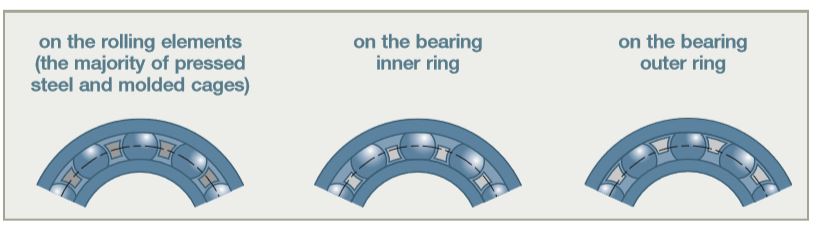
The centering choice depends on the bearing operating criteria: vibration, impacts, high speeds, speed variations,…
-Choice of a special cage
The choice of a special cage will depend on the particular bearing operating criteria: Temperature, lubrication, vibration, sudden acceleration and deceleration, shaft-housing misalignment. See the table on the opposite page.
In certain applications where a substantial increase in the dynamic loading capacity is needed (speed reducers, gearboxes, etc.) or static loading capacity (rollers, pulleys, etc.) special cageless bearings can be used.
It should be noted that the maximum speed for this type of bearing is lower than that of the corresponding standard bearing. Its lubrication demands a certain amount of attention due to the relative friction of the rolling elements.


